
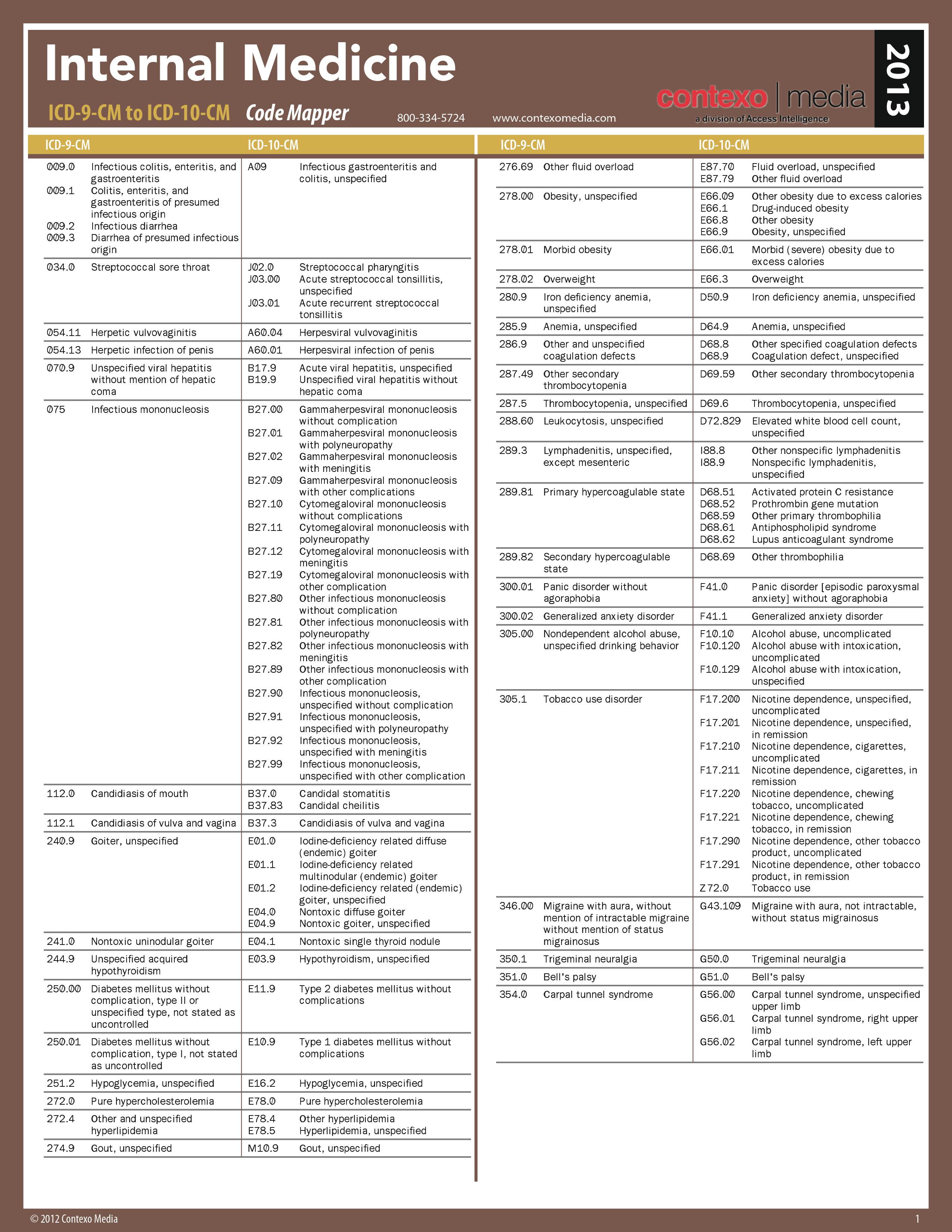
The prognosis improves if vigorous treatment begins immediately. Mortality is high when treatment is delayed and almost one-half of sudden deaths due to an MI occur before hospitalization, within one hour of the onset of symptoms. The ACS continuum representing ongoing myocardial ischemia or injury consists of unstable angina, non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), and ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI).Ĭardiovascular diseases, the leading cause of death in the United States and Western Europe usually result from cardiac damage or complications of MI. Myocardial infarction is a part of a broader category of a disease known as acute coronary syndrome (ACS), resulting from prolonged myocardial ischemia due to reduced blood flow through one of the coronary arteries. This usually results from an imbalance in oxygen supply and demand, which is most often caused by plaque rupture with thrombus formation in a coronary vessel, resulting in an acute reduction of blood supply to a portion of the myocardium (Zafari, 2015). Myocardial infarction (MI) or acute myocardial infarction (AMI) commonly known as heart attack, is the irreversible necrosis of heart muscle secondary to prolonged ischemia. Improving Tissue Perfusion & Initiating Cardiac Rehabilitation
Improving Cardiac Output & Monitoring Potential Complications
Administering Medication and Pharmacologic Support Initiating Pain Relief and Ischemia & Improving Respiratory Function


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
